In this tutorial we will learn How to make out PIC projects wireless by interfacing a Bluetooth Module (HC-06). where we have started from the scratch, like learning MPLAB and XC8, interfacing LED, LCD, using Timers, ADC, PWM etc.
Here, we have used the popular Bluetooth module HC-06. Using this module we can receive and send information wirelessly from our PIC MCU to a mobile application or a computer. Communication between PIC and HC-06 is established using the USART module present in the PIC Microcontroller. You can also use the HC-05. We again operate on the same Asynchronous 8-bit mode, but this time we will modify our code a bit so that it works with the Bluetooth module. Hence learning UART tutorial beforehand is an added advantage for this project.
In this tutorial, we will toggle a LED by sending on or off command from our Smart phone. We will use an Android application called Bluetooth Terminal which can send and receive data over Bluetooth. If we send a char ‘1’ from the app the light will be turned ON in the PIC board and we will get an acknowledgment back to the phone that the light has been turned on. Similarly we can send ‘0’ from phone to turn it off. This way we can control the LED light on our PIC board, similar to the UART tutorial but now wirelessly. Complete Program and the Detailed Video is given at the end of this tutorial.
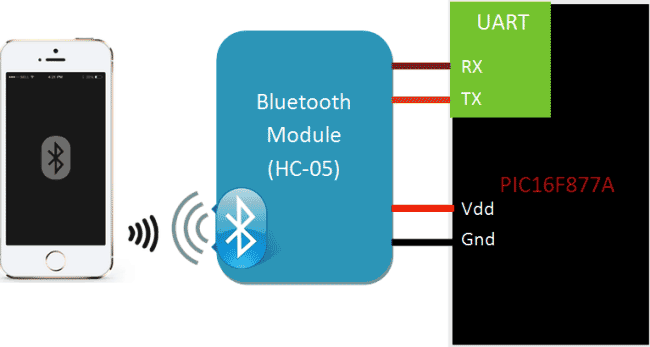
The basic block diagram for the setup is shown below.
Requirements:
Hardware:
- PIC16F877A Perf Board
- HC-05 or HC-06 Bluetooth Module
- Computer (for programming )
- Mobile Phone
- PICkit 3 Programmer
Software:
Bluetooth Module HC-06:
Bluetooth can operate in the following two modes:
- Command Mode
- Operating Mode
In Command Mode we will be able to configure the Bluetooth properties like the name of the Bluetooth signal, its password, the operating baud rate etc. The Operating Mode is the one in which we will be able to send and receive data between the PIC Microcontroller and the Bluetooth module. Hence in this tutorial we will be toying only with the Operating Mode. The Command mode will be left to the default settings. The Device name will be HC-05 (I am using HC-06) and the password will be 0000 or 1234 and most importantly the default baud rate for all Bluetooth modules will be 9600.

The module works on 5V supply and the signal pins operate on 3.3V, hence a 3.3V regulator is present in the module itself. Hence we need not worry about it. Out of the six pins only four will be used in the Operating mode. The pin connection table is shown below
S.No
|
Pin on HC-05/HC-06
|
Pin name on MCU
|
Pin number in PIC
|
1
|
Vcc
|
Vdd
|
31st pin
|
2
|
Vcc
|
Gnd
|
32nd pin
|
3
|
Tx
|
RC6/Tx/CK
|
25th pin
|
4
|
Rx
|
RC7/Rx/DT
|
26th pin
|
5
|
State
|
NC
|
NC
|
6
|
EN (Enable)
|
NC
|
NC
|
Programming PIC Microcontroller for Bluetooth Communication:
Like all modules (ADC, Timer, PWM) we should also initialize our Bluetooth module. The initialization will be similar to UART initialization but we need to make some changes for the Bluetooth to work flawlessly with our PIC16F877A MCU. Let’s define the configuration bits and start with the Bluetooth initialization function.
Initializing Bluetooth:
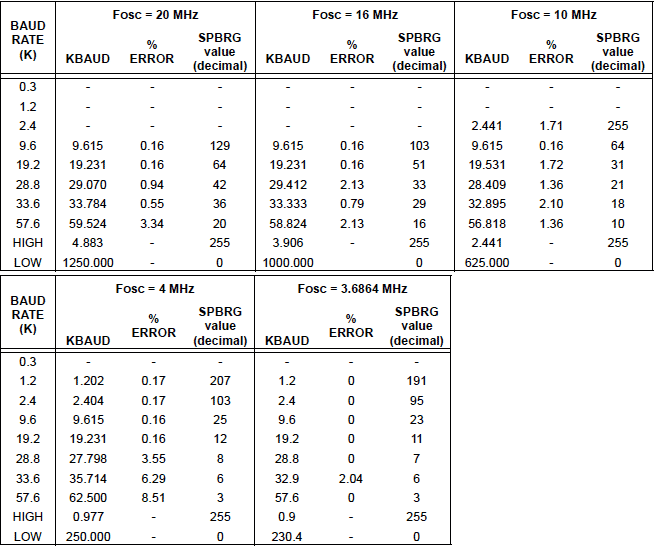
Almost all the Bluetooth modules in the market work at a baud rate of 9600, it is very important to set your baud rate same as that of Bluetooth modules operating baud rate, here we set SPBRG=129 since we are operating at 20Mhz clock frequency with 9600 as baud rate. Hence the above initialization will work only for Bluetooth modules operating at 9600 baud rate. It is also mandatory to have the high speed baud rate bit BRGH enabled. This will help in setting an accurate baud rate.
//******Initialize Bluetooth using USART********//
void Initialize_Bluetooth()
{
//Set the pins of RX and TX//
TRISC6=1;
TRISC7=1;
//Set the baud rate using the look up table in datasheet(pg114)//
BRGH=1; //Always use high speed baud rate with Bluetooth else it wont work
SPBRG =129;
//Turn on Asyc. Serial Port//
SYNC=0;
SPEN=1;
//Set 8-bit reception and transmission
RX9=0;
TX9=0;
//Enable transmission and reception//
TXEN=1;
CREN=1;
//Enable global and ph. interrupts//
GIE = 1;
PEIE= 1;
//Enable interrupts for Tx. and Rx.//
RCIE=1;
TXIE=1;
}
//___________BT initialized_____________//
If you have a BT module which operates at a different baud rate, then you can refer the look up table below to find out your value for the SPBRG.
Loading data into Bluetooth:
Once the function is initialized we have three functions in our program to send and receive data from Bluetooth. Unlike UART we have few things to consider here before we can transmit or receive data. The Bluetooth module has a Transmit and Receive buffer inside it, the data sent to it will be stored in the Tx buffer. This data will not be broadcasted (sent on air) unless a carriage return is sent to the module. Hence in order to transmit data we have to load the Rx buffer of BT and then broadcast it using carriage return.
The above working can be easily achieved by using the following functions. The below function can be used when we have to load only one character into the Rx buffer. We load the data into the TXREG register and wait till it is processed by check on the flag TXIF and TRMT by using while loops.
//Function to load the Bluetooth Rx. buffer with one char.//
void BT_load_char(char byte)
{
TXREG = byte;
while(!TXIF);
while(!TRMT);
}
//End of function//
Below function is used to load a string into the Rx buffer of the Bluetooth module. The string is split into characters and each character is sent to the BT_load_char() function.
//Function to Load Bluetooth Rx. buffer with string//
void BT_load_string(char* string)
{
while(*string)
BT_load_char(*string++);
}
//End of function/
Broadcasting data over Bluetooth:
Till now we have just transmitted information into the Rx buffer of the HC-05 module. Now we must instruct it to broadcast the data over air by using this function.
//Function to broadcast data from RX. buffer//
void broadcast_BT()
{
TXREG = 13;
__delay_ms(500);
}
//End of function//
In this function we send a value 13 into the TXREG register. This value 13 is nothing but the decimal equivalent for carriage (refer ASCII chart). Then a small delay is created for the broadcaster to start.
Reading data from Bluetooth:
Similar to UART, the below function is used to read data from the Bluetooth
//Function to get a char from Rx.buffer of BT//
char BT_get_char(void)
{
if(OERR) // check for over run error
{
CREN = 0;
CREN = 1; //Reset CREN
}
if(RCIF==1) //if the user has sent a char return the char (ASCII value)
{
while(!RCIF);
return RCREG;
}
else //if user has sent no message return 0
return 0;
}
//End of function/
If the user has sent a data, this function will return that particular data which can be saved in a variable and processed. If the user has not sent anything the function will return zero.
Main function:
We have used all the above explained functions inside or main function. We send some introductory message and then wait for the user to send some values based on which we toggle the RED led light connected to the RB3 pin on our Perf board.
void main(void)
{
//Scope variable declarations//
int get_value;
//End of variable declaration//
//I/O Declarations//
TRISB3=0;
//End of I/O declaration//
Initialize_Bluetooth(); //lets get our bluetooth ready for action
//Show some introductory message once on power up//
BT_load_string("Bluetooth Initialized and Ready");
broadcast_BT();
BT_load_string("Press 1 to turn ON LED");
broadcast_BT();
BT_load_string("Press 0 to turn OFF LED");
broadcast_BT();
//End of message//
while(1) //The infinite lop
{
get_value = BT_get_char(); //Read the char. received via BT
//If we receive a '0'//
if (get_value=='0')
{
RB3=0;
BT_load_string("LED turned OFF");
broadcast_BT();
}
//If we receive a '1'//
if (get_value=='1')
{
RB3=1;
BT_load_string("LED turned ON");
broadcast_BT();
}
}
}
Check the Full Program in the Code Section Below.
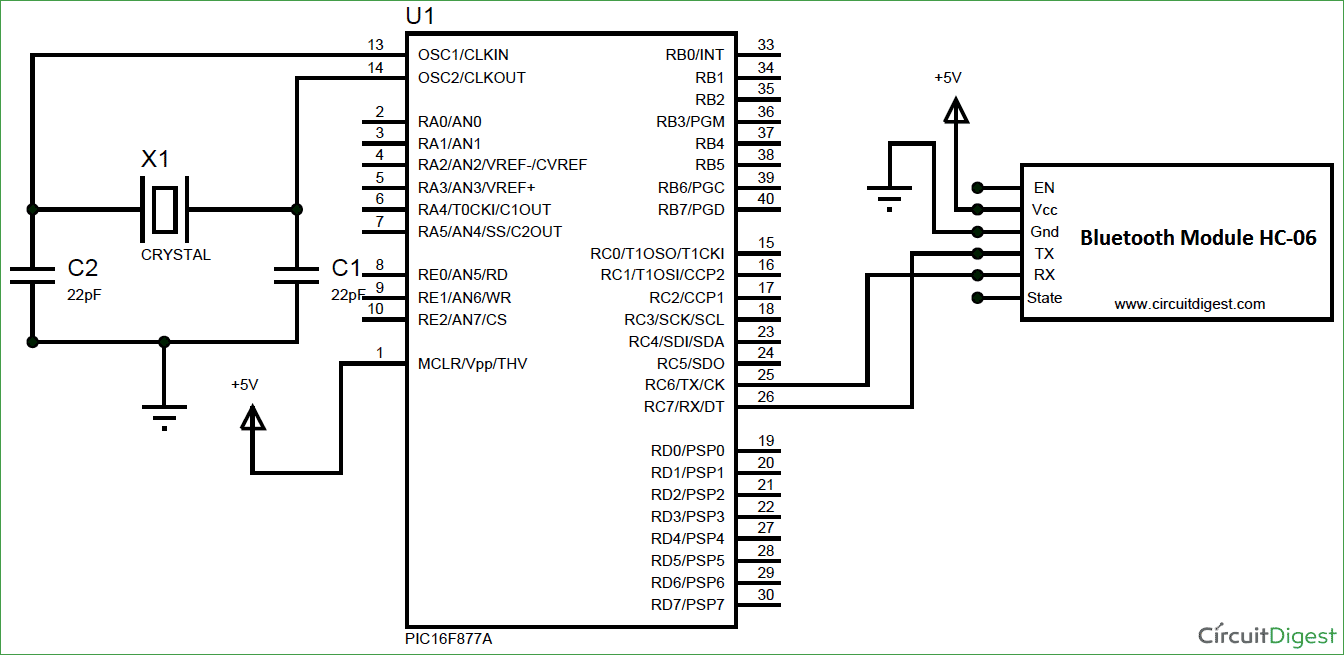
Circuit Diagram and Hardware Setup:
Circuit connections for this project is very simple, we simply have to power up the Bluetooth module and connect the Tx to the 26th pin of PIC and Rx to the 25th pin of PIC as shown in the circuit diagram below:
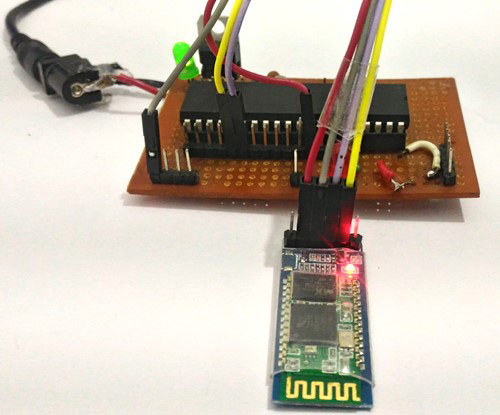
Now let us proceed to the hardware. Once the connection is done it should look something like this.
Controlling LED using Bluetooth Mobile Application:
Now let us get our Android application ready. Download the application called Bluetooth Terminal from the App store or use this link. Once the application is downloaded and installed, turn on your PIC perf board which we are using since beginning. The small LED light on your Bluetooth Module should be flashing to indicate that it is powered on and is actively looking for a phone to establish a connection.
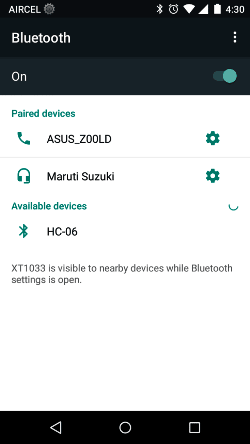
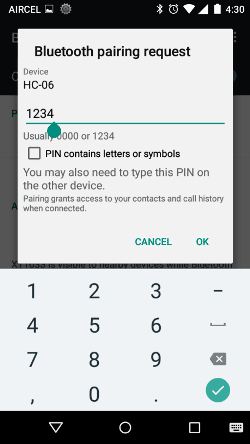
Now get into the Bluetooth Settings of your phone and search for new Bluetooth device you should be able to see the name HC-05 or HC-06 based on your module. I am using HC-06 hence my phone shows the following display. Then try paring with it and it will ask for a password. Enter the password as 1234 (for some it might be 0000) and click OK as shown below.
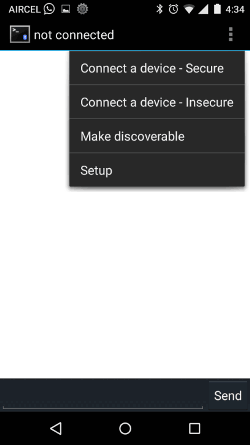
After the paring is successful, open the Bluetooth Terminal application that we just installed. Get into the settings option and select “Connect a device – Secure” as shown below. This will open a pop box where all our paired devices will be listed as shown below. Select the HC-05 or HC-06 module.
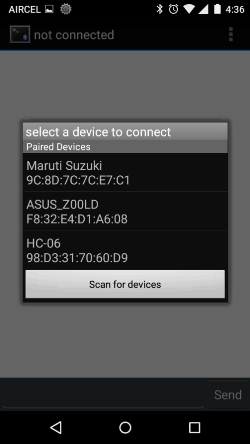
Once the connection is established, the light on the Bluetooth module which was flashing so far must have become constant to indicate that it has successfully connected to your mobile. And we should get the introductory message from our Program like shown below.
Now press ‘1’ to turn on the LED light and press ‘0’ to turn off the light. The complete working will be shown in the Video. Your mobile screen will look something like this shown below.


So that is it guys, we have learnt How to Interface Bluetooth module to our PIC microcontroller, now with the aid of this we can try wireless projects. There are lots of projects which uses Bluetooth, you can try them or come up with your own Idea and do share them in the comment section. Also check our previous project with Bluetooth terminal app and HC-05 like Smart Phone Controlled Home Automation Using Arduino and Smart Phone Controlled Digital Code Lock using Arduino.
Hope, this tutorial helped you! If you got stuck somewhere, kindly use the comment section.
Code:
// CONFIG
#pragma config FOSC = HS // Oscillator Selection bits (HS oscillator)
#pragma config WDTE = OFF // Watchdog Timer Enable bit (WDT disabled)
#pragma config PWRTE = OFF // Power-up Timer Enable bit (PWRT enabled)
#pragma config BOREN = OFF // Brown-out Reset Enable bit (BOR enabled)
#pragma config LVP = OFF // Low-Voltage (Single-Supply) In-Circuit Serial Programming Enable bit (RB3 is digital I/O, HV on MCLR must be used for programming)
#pragma config CPD = OFF // Data EEPROM Memory Code Protection bit (Data EEPROM code protection off)
#pragma config WRT = OFF // Flash Program Memory Write Enable bits (Write protection off; all program memory may be written to by EECON control)
#pragma config CP = OFF // Flash Program Memory Code Protection bit (Code protection off)
//End of CONFIG registers
#pragma config FOSC = HS // Oscillator Selection bits (HS oscillator)
#pragma config WDTE = OFF // Watchdog Timer Enable bit (WDT disabled)
#pragma config PWRTE = OFF // Power-up Timer Enable bit (PWRT enabled)
#pragma config BOREN = OFF // Brown-out Reset Enable bit (BOR enabled)
#pragma config LVP = OFF // Low-Voltage (Single-Supply) In-Circuit Serial Programming Enable bit (RB3 is digital I/O, HV on MCLR must be used for programming)
#pragma config CPD = OFF // Data EEPROM Memory Code Protection bit (Data EEPROM code protection off)
#pragma config WRT = OFF // Flash Program Memory Write Enable bits (Write protection off; all program memory may be written to by EECON control)
#pragma config CP = OFF // Flash Program Memory Code Protection bit (Code protection off)
//End of CONFIG registers
#define _XTAL_FREQ 20000000
#include<xc.h>
#include<xc.h>
//******Initialize Bluetooth using USART********//
void Initialize_Bluetooth()
{
//Set the pins of RX and TX//
TRISC6=1;
TRISC7=1;
//Set the baud rate using the look up table in datasheet(pg114)//
BRGH=1; //Always use high speed baud rate with Bluetooth else it wont work
SPBRG =129;
//Turn on Asyc. Serial Port//
SYNC=0;
SPEN=1;
//Set 8-bit reception and transmission
RX9=0;
TX9=0;
void Initialize_Bluetooth()
{
//Set the pins of RX and TX//
TRISC6=1;
TRISC7=1;
//Set the baud rate using the look up table in datasheet(pg114)//
BRGH=1; //Always use high speed baud rate with Bluetooth else it wont work
SPBRG =129;
//Turn on Asyc. Serial Port//
SYNC=0;
SPEN=1;
//Set 8-bit reception and transmission
RX9=0;
TX9=0;
//Enable transmission and reception//
TXEN=1;
CREN=1;
//Enable global and ph. interrupts//
GIE = 1;
PEIE= 1;
//Enable interrupts for Tx. and Rx.//
RCIE=1;
TXIE=1;
}
//___________BT initialized_____________//
TXEN=1;
CREN=1;
//Enable global and ph. interrupts//
GIE = 1;
PEIE= 1;
//Enable interrupts for Tx. and Rx.//
RCIE=1;
TXIE=1;
}
//___________BT initialized_____________//
//Function to load the Bluetooth Rx. buffer with one char.//
void BT_load_char(char byte)
{
TXREG = byte;
while(!TXIF);
while(!TRMT);
}
//End of function//
void BT_load_char(char byte)
{
TXREG = byte;
while(!TXIF);
while(!TRMT);
}
//End of function//
//Function to Load Bluetooth Rx. buffer with string//
void BT_load_string(char* string)
{
while(*string)
BT_load_char(*string++);
}
//End of function//
void BT_load_string(char* string)
{
while(*string)
BT_load_char(*string++);
}
//End of function//
//Function to broadcast data from RX. buffer//
void broadcast_BT()
{
TXREG = 13;
__delay_ms(500);
}
//End of function//
void broadcast_BT()
{
TXREG = 13;
__delay_ms(500);
}
//End of function//
//Function to get a char from Rx.buffer of BT//
char BT_get_char(void)
{
if(OERR) // check for over run error
{
CREN = 0;
CREN = 1; //Reset CREN
}
if(RCIF==1) //if the user has sent a char return the char (ASCII value)
{
while(!RCIF);
return RCREG;
}
else //if user has sent no message return 0
return 0;
}
//End of function/
char BT_get_char(void)
{
if(OERR) // check for over run error
{
CREN = 0;
CREN = 1; //Reset CREN
}
if(RCIF==1) //if the user has sent a char return the char (ASCII value)
{
while(!RCIF);
return RCREG;
}
else //if user has sent no message return 0
return 0;
}
//End of function/
void main(void)
{
//Scope variable declarations//
int get_value;
//End of variable declaration//
//I/O Declarations//
TRISB3=0;
//End of I/O declaration//
Initialize_Bluetooth(); //lets get our bluetooth ready for action
//Show some introductory message once on power up//
BT_load_string("Bluetooth Initialized and Ready");
broadcast_BT();
BT_load_string("Press 1 to turn ON LED");
broadcast_BT();
BT_load_string("Press 0 to turn OFF LED");
broadcast_BT();
//End of message//
while(1) //The infinite lop
{
get_value = BT_get_char(); //Read the char. received via BT
//If we receive a '0'//
if (get_value=='0')
{
RB3=0;
BT_load_string("LED turned OFF");
broadcast_BT();
}
//If we receive a '1'//
if (get_value=='1')
{
RB3=1;
BT_load_string("LED turned ON");
broadcast_BT();
}
}
}
{
//Scope variable declarations//
int get_value;
//End of variable declaration//
//I/O Declarations//
TRISB3=0;
//End of I/O declaration//
Initialize_Bluetooth(); //lets get our bluetooth ready for action
//Show some introductory message once on power up//
BT_load_string("Bluetooth Initialized and Ready");
broadcast_BT();
BT_load_string("Press 1 to turn ON LED");
broadcast_BT();
BT_load_string("Press 0 to turn OFF LED");
broadcast_BT();
//End of message//
while(1) //The infinite lop
{
get_value = BT_get_char(); //Read the char. received via BT
//If we receive a '0'//
if (get_value=='0')
{
RB3=0;
BT_load_string("LED turned OFF");
broadcast_BT();
}
//If we receive a '1'//
if (get_value=='1')
{
RB3=1;
BT_load_string("LED turned ON");
broadcast_BT();
}
}
}
No comments:
Post a Comment